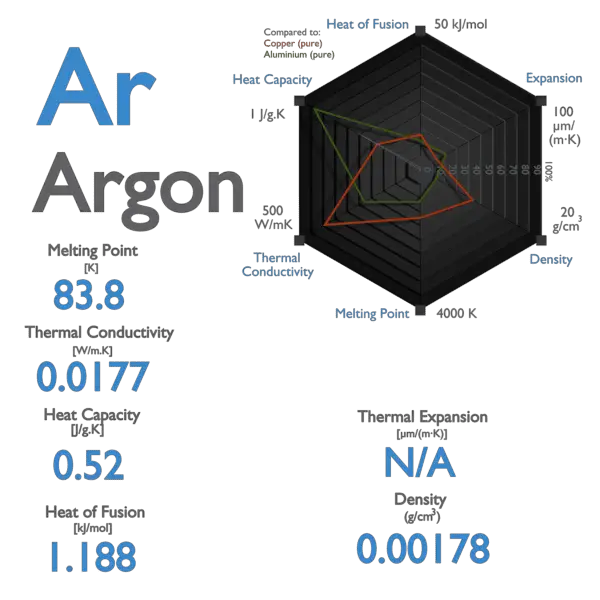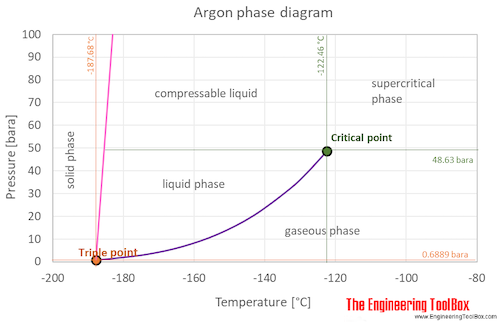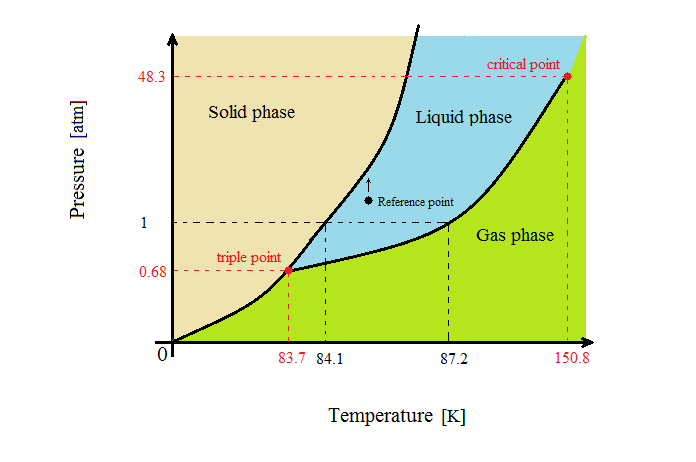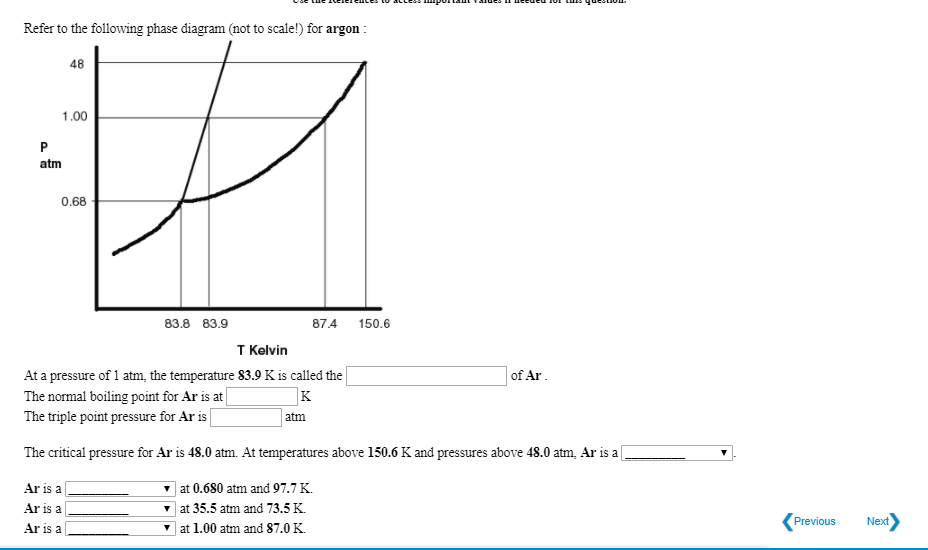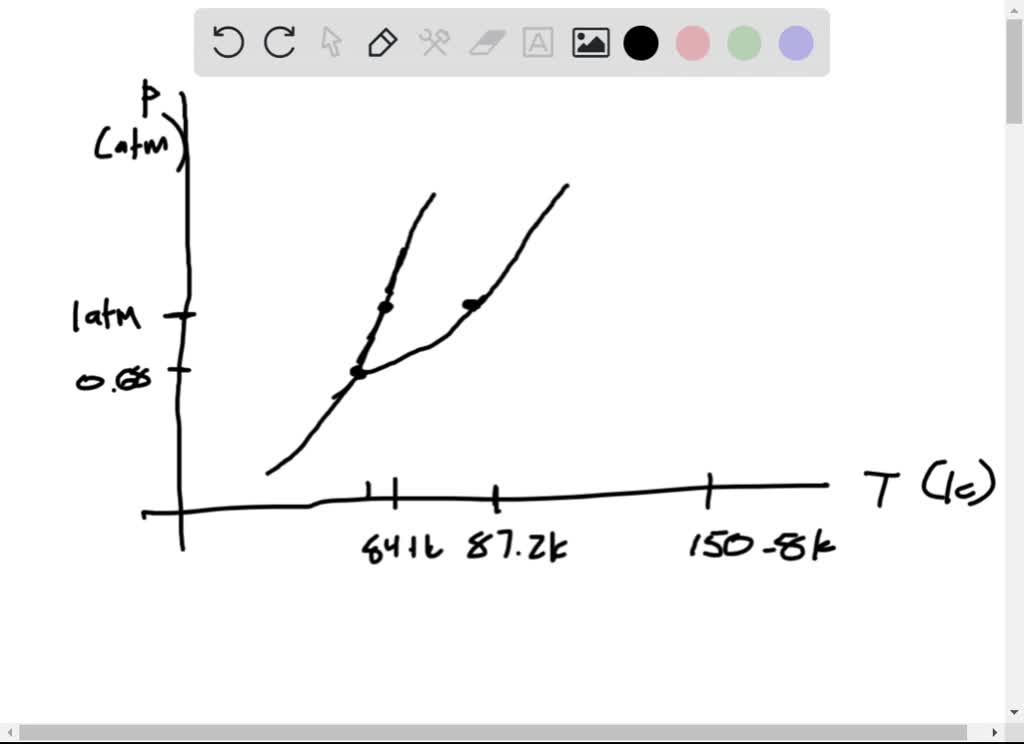
SOLVED: Argon has a normal boiling point of 87.2 K and a melting point (at 1 atm) of 84.1 K. Its critical temperature is 150.8 K, and its critical pressure is 48.3

Argon. Edelgase. Chemisches Element des Mendelejew Periodensystems. Argon im quadratischen Würfel kreatives Konzept. 3D-Illustration Stockfotografie - Alamy
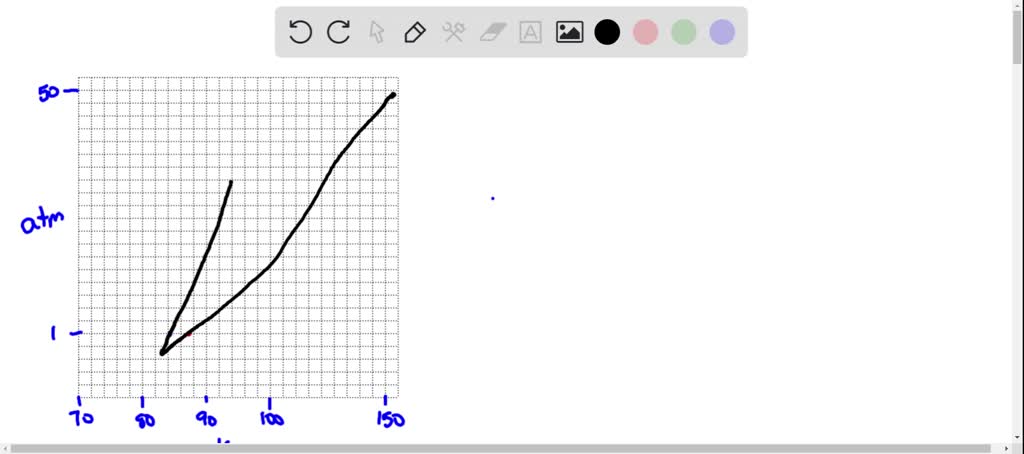
SOLVED: Argon has a normal boiling point of 87.2 K and a melting point (at 1 atm) of 84.1 K. Its critical temperature is 150.8 K, and its critical pressure is 48.3
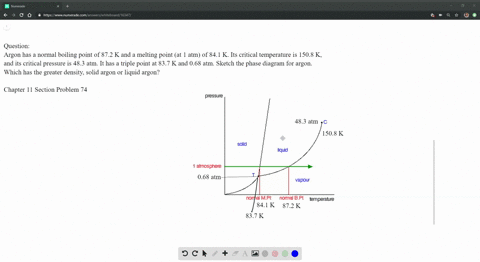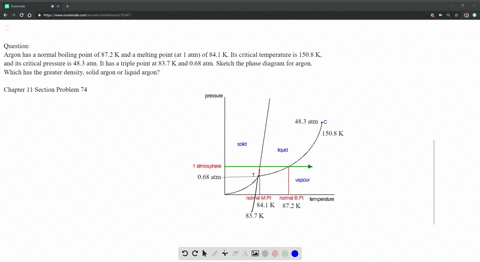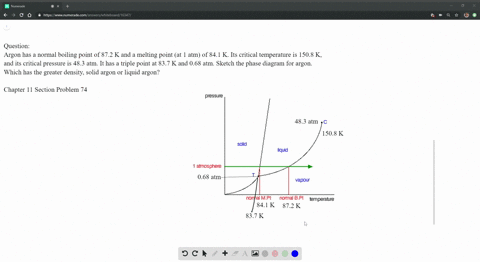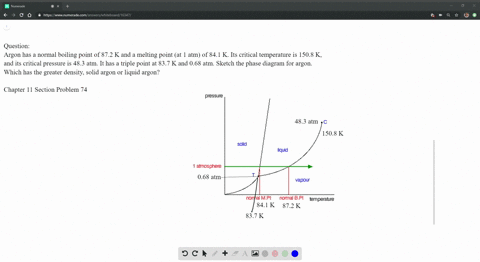
SOLVED: Argon has a normal boiling point of 87.2 K and a melting point (at 1 atm) of 84.1 K. Its critical temperature is 150.8 K, and its critical pressure is 48.3

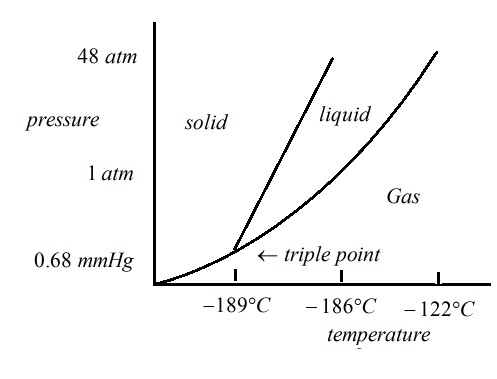
Sketch the phase diagram of argon, Ar, from the following information: normal melting point, -187 degrees C; normal boiling point, -186 degrees C; triple point, -189 degrees C, 0.68 atm; critical point, -